What is a Contract Type in CLM?
🗺️ Overview
In CLM, Contract Types are used to classify contracts by their business purpose, while Templates define how those contracts are structured. The system provides a set of predefined contract types and allows power users to create additional custom types as needed.
Each contract type is always linked to one or more templates. This ensures that contracts are created using approved structures, documents, and attributes, and that users are guided to the correct starting point when creating a contract.
🎯 Purpose
The purpose of linking contract types to templates is to combine flexibility with governance. Contract types provide a clear classification of agreements, while templates enforce consistent structure, content, and rules for contract creation.
This approach ensures that every contract follows an approved format, while still allowing organizations to support different regions, business units, or contract scenarios through multiple templates under the same contract type.
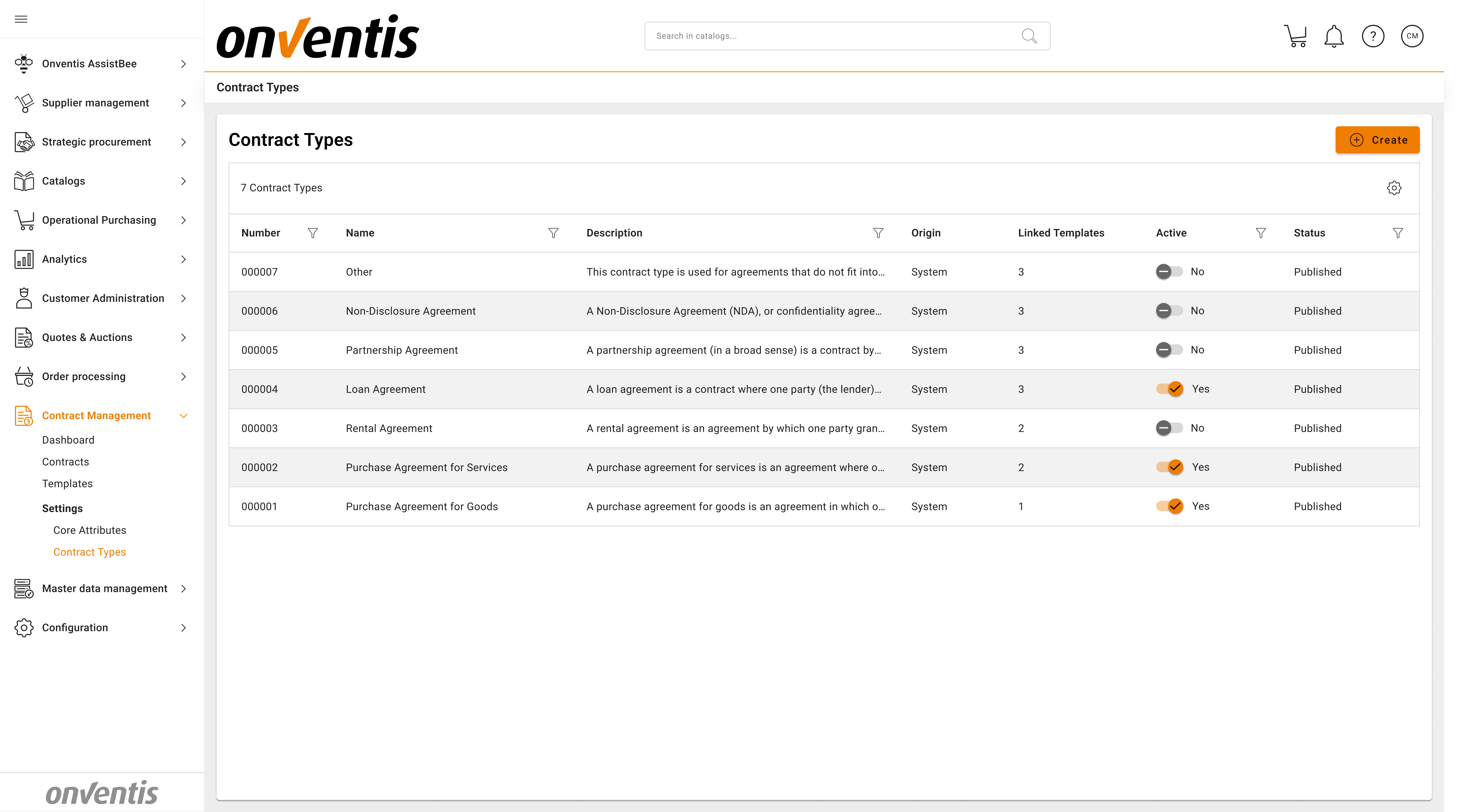
🧱 Standard Contract Types
The system comes with five core contract types available out of the box:
Contract Type | Description |
|---|---|
Purchase Agreement for Goods | A purchase agreement for goods is an agreement in which one party (the seller) agrees to transfer ownership of goods or other property to another (the buyer) for a price. It is the classic contract type for trade. Sales can cover movable goods, immovable property, rights, or other valuable assets. |
Purchase Agreement for Services | A purchase agreement for services is an agreement where one party (the service provider) undertakes to perform services or tasks for another party (the buyer or client) in exchange for payment. Unlike a sale, the object is not a transfer of a tangible thing but the rendering of intangible work or effort. Service agreements can take different forms: in civil law, a classic distinction is made between a service contract in the narrow sense and a contract to produce a specific work/result. In a pure service contract, the provider owes their best efforts or activity (e.g. consulting, IT support, maintenance) but not a guaranteed outcome. In a work contract, the provider commits to deliver a concrete result or work product (e.g. a construction project, a software implementation with defined features) and is responsible for achieving that result. Both fall under the broad category of services in a business context. |
Software | Used for software license, maintenance, or SaaS-related agreements. |
Rental Agreement | A rental agreement is an agreement by which one party grants another party the right to use an asset in exchange for payment, for a defined period, without transferring ownership. There are various sub-forms (e.g. commercial rent of office space, equipment rent, software rent, etc.), but all share the basic pattern of use-against-payment over time. |
Loan Agreement | A loan agreement is a contract where one party (the lender) provides money (or other fungible assets) to another party (the borrower), and the borrower agrees to repay the same amount (often with interest) at a later date. In legal terms, the lender temporarily transfers disposal of a sum of money (or replaceable goods) to the borrower, who owes repayment in due course. Key features are the principal amount, interest rate, term (duration) and repayment schedule. This category includes credit agreements, credit lines, promissory note loans, inter-company loans, and similar financial contracts. (It does not include equity investment agreements, which are partnership/shareholder in nature—those are covered under partnership agreement) |
Partnership Agreement | A partnership agreement (in a broad sense) is a contract by which two or more parties agree to cooperate and combine resources/efforts to achieve a common goal, sharing the results (profits or losses). This can create a partnership entity or a purely contractual joint venture. A joint venture (JV) agreement typically refers to a contract between businesses to undertake a specific project or form a new jointly-owned company – it might be structured either as a partnership or via setting up a separate legal entity (with a shareholders’ agreement). In either case, the contract defines each party’s contributions, governance of the venture, profit-sharing, decision-making, and exit strategy. |
Other | A flexible contract type used when no predefined template fits. Typically for ad-hoc or one-off agreements. |
🧩 Note: Standard contract types are system-delivered and cannot be edited or deleted.
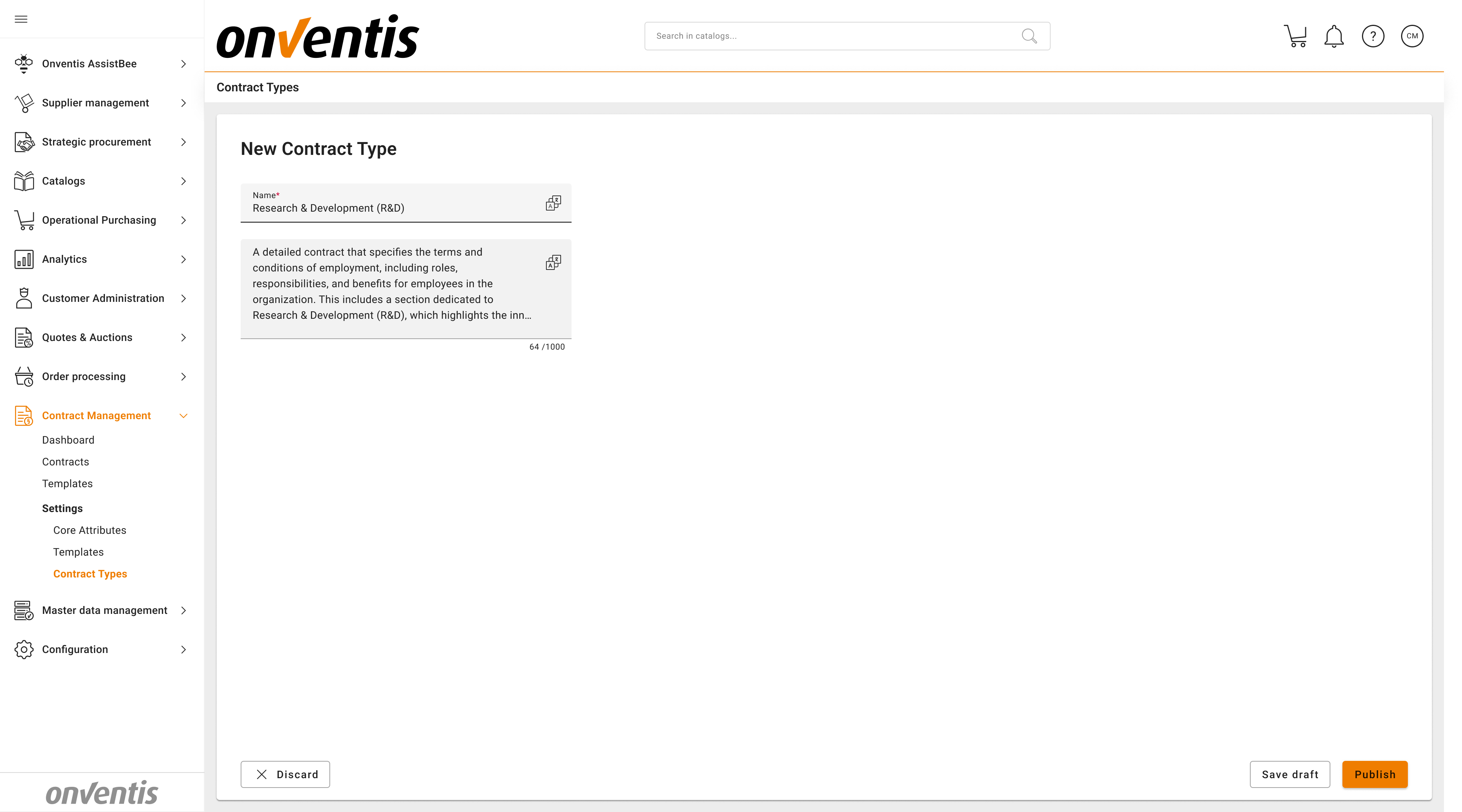
🛠️ Custom Contract Types
CLM Power Users can create new contract types to fit organizational needs.
For example, you may add:
“Research & Development (R&D)”
“Licensing”
“Leasing”
Custom contract types allow organizations to align contract structure and content with internal policies or industry-specific standards.
Contract types have its own lifecycle, same as the Templates (it has Draft and Published status).
📁 Templates and Document Standards
Each contract template in the system is linked to a specific contract type.
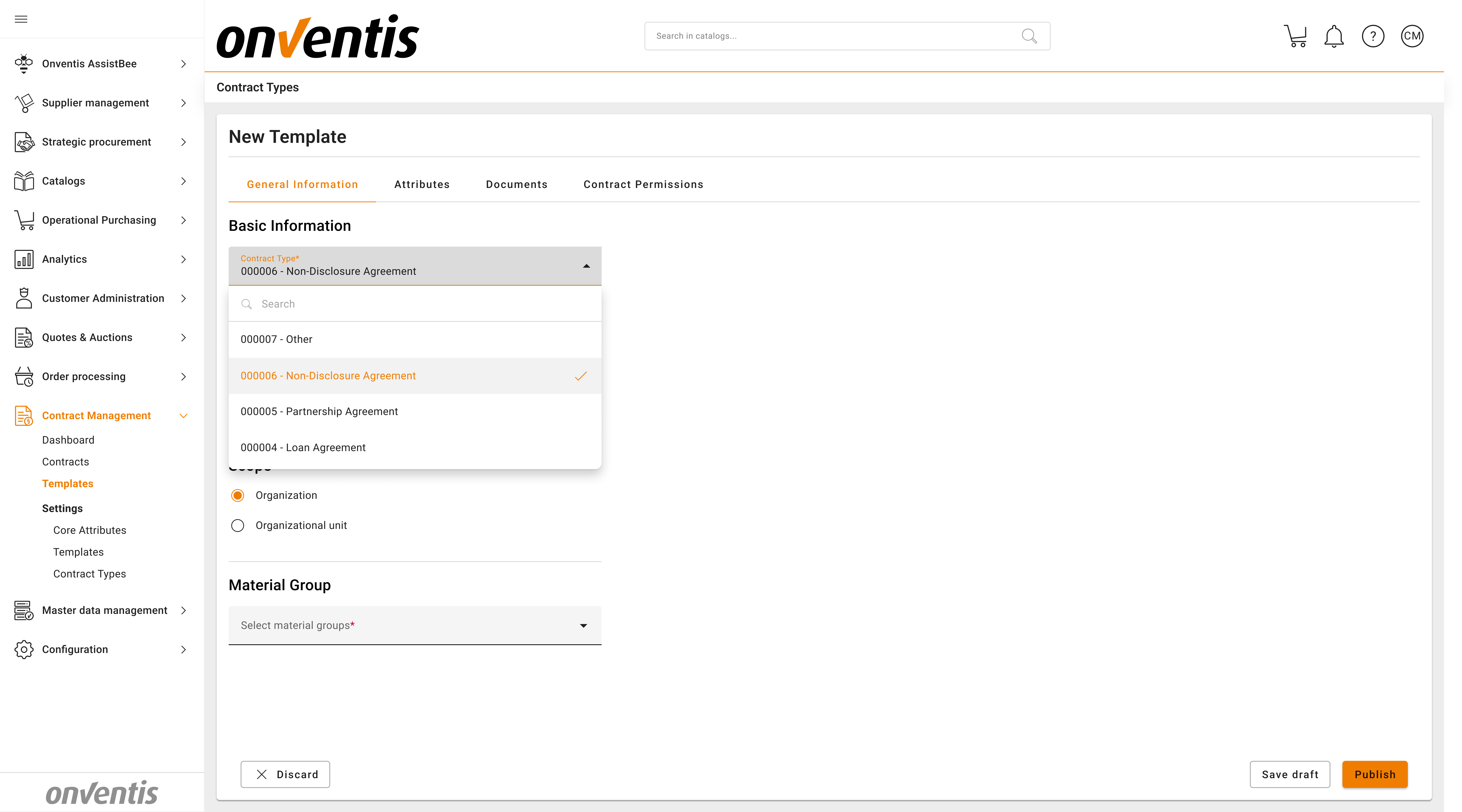
When a template is selected, it automatically includes a document standard, forming a structured binder of related documents.
Example Binder:
Document | Description |
|---|---|
Main Agreement | Core contractual terms |
Appendix 1 | Scope of Work (SOW) |
Appendix 2 | Pricing or Financial Terms |
Appendix 3 | Technical Specifications |
NDA | Confidentiality agreement |
GDPR Addendum | Data processing obligations |
SLA | Service Level Agreement |
Users can directly edit these documents, update relevant data, and proceed to signature — saving significant preparation time.
⚙️ Step-by-Step Flow
Power user reviews the system contract types
→ Creates templates for Organization or Organization unit scope and links to standard contract typesPower user creates custom contact types
→ Creates templates for Organization or Organization unit scope and links to custom contract typesPower User creates the contract from a Template
→ Power User selects the contract type first, after that the list of templates linked to the contact type will become selectable
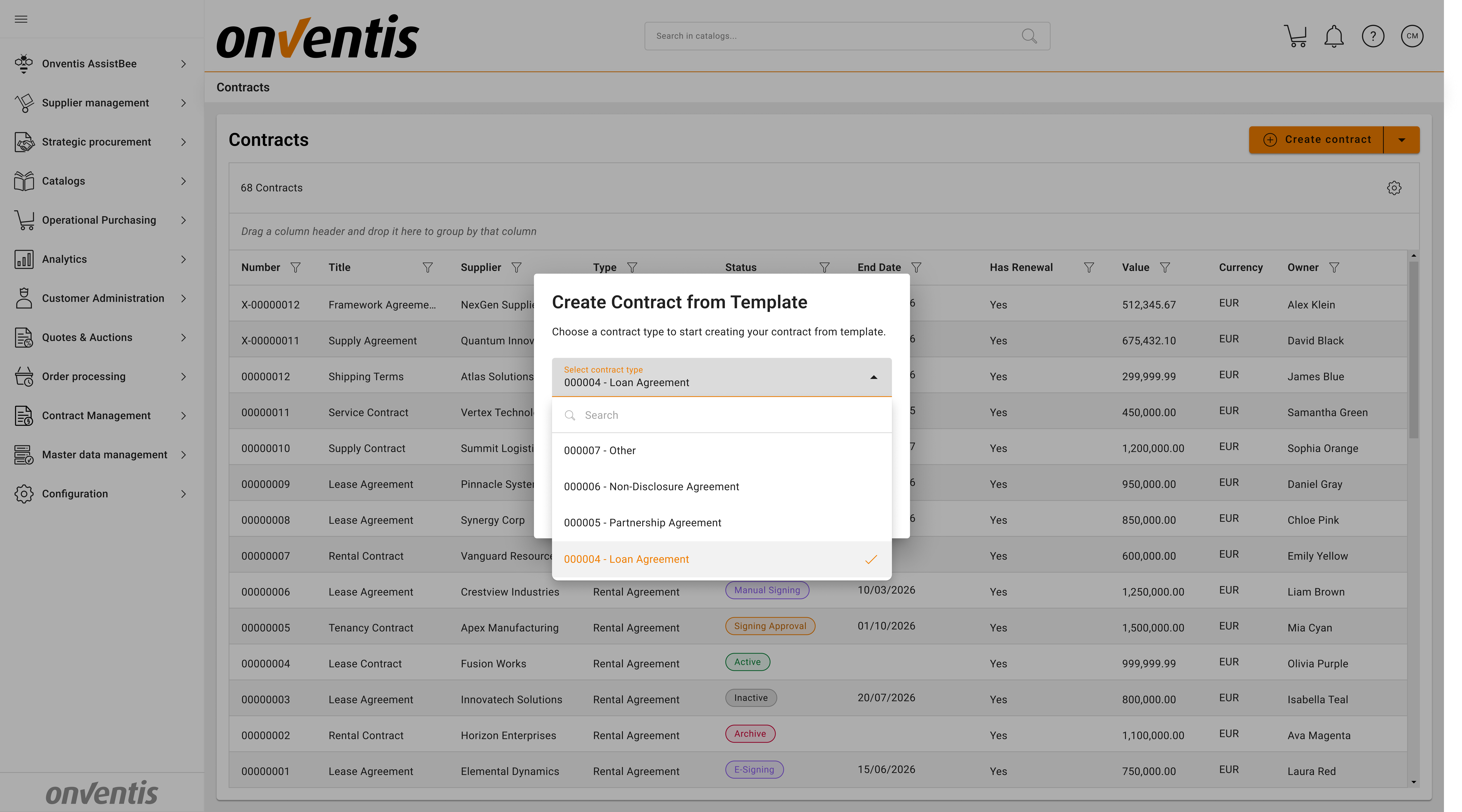
Template and binder are applied automatically
→ Pre-populated structure appears in the contract workspace.
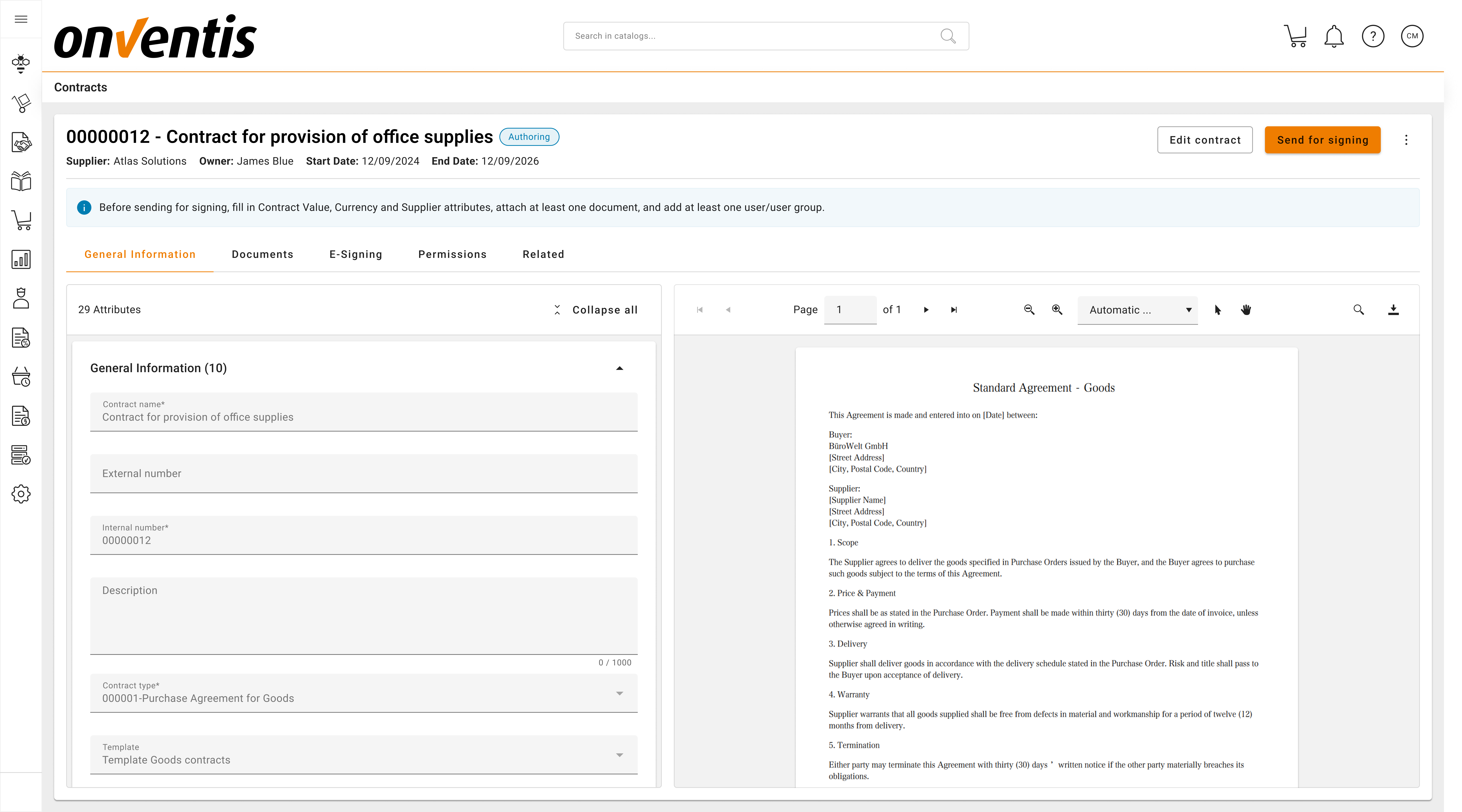
Power User reviews and edits content
→ Updates key fields and attached documents.Contract proceeds to next Steps in the lifecycle.
💡 Benefits
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Flexibility | Allows multiple templates per contract type to support variations such as regions, business units, or risk levels, without creating unnecessary contract types |
Consistency | Ensures that all contracts of the same type are created using approved templates, resulting in consistent structure, content, and data across the contract portfolio |
Reduced errors | Keeps contract types focused on classification and reporting, while templates define structure, documents, and attributes. This simplifies configuration and maintenance. |
Scalability | Supports growing contract volumes by enforcing consistent rules and structures, without increasing administrative overhead. No limitations to the number of custom contract types creation. |
Governance | Prevents creation of unstructured or incomplete contracts by guiding users to predefined templates linked to each contract type. |
🔐 Permissions and Editing Rules
Only CLM Power Users can create, modify, or delete custom contract types.
Standard contract types (Purchase Agreement for Goods, Purchase Agreement for Services, etc.) are locked and cannot be changed.
Contract types are visible to all users when creating a new contract.
Templates must be assigned to exactly one contract type.
Best Practices
💡 Tips for Effective Use:
Use system contract types for common and standardized agreements.
Create custom contract types only when a clear business need exists.
Link each contract type to at least one approved template.
Use multiple templates under the same contract type to handle variations rather than creating many similar contract types.
Manage attributes, documents, and permissions at template level to ensure consistent inheritance.
Review and maintain templates regularly to keep contract creation aligned with current policies.
